In this article, we will learn the concept of iDoc status and its purpose. Then we will identify the categories of iDoc statuses and look at a full list of inbound and outbound iDoc status codes. Additionally, we will see the sequence of iDoc statuses for both inbound and outbound iDoc processing.
Moreover, we will go through iDoc status monitoring tools of SAP such as AIF, BD87, and We02. Also, how to change an iDoc status manually. Finally, we will take a deep dive into a few important iDoc statuses such as status 51, status 53, status 64, status 1, status 30, etc.
The concept of iDoc Status
When an iDoc is being processed, it passes through a series of events or steps. The outcome of each processing step is denoted by a two-digit number. For example, the successful creation of an inbound iDoc is denoted by status 50, “Doc added”. If the incoming iDoc creates the application document successfully, iDoc goes into status 53, “Application document posted”.
Each of these milestones of an iDoc is logged into the iDoc status record. Hence, iDoc statuses allow the processing of the iDoc to be monitored. Additionally, iDoc status plays a key role when it comes to troubleshooting iDoc issues as it tells you if the processing event ended up in an error, was processed successfully, or was processed with errors.
The last status code of the iDoc is known as the final status; it is a part of the iDoc control record.
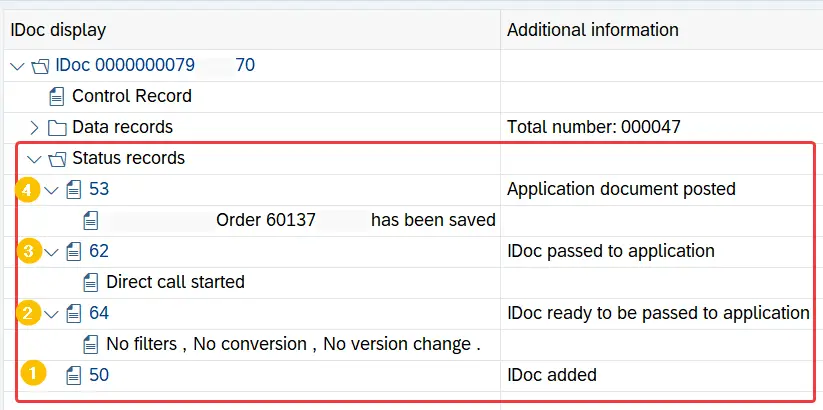
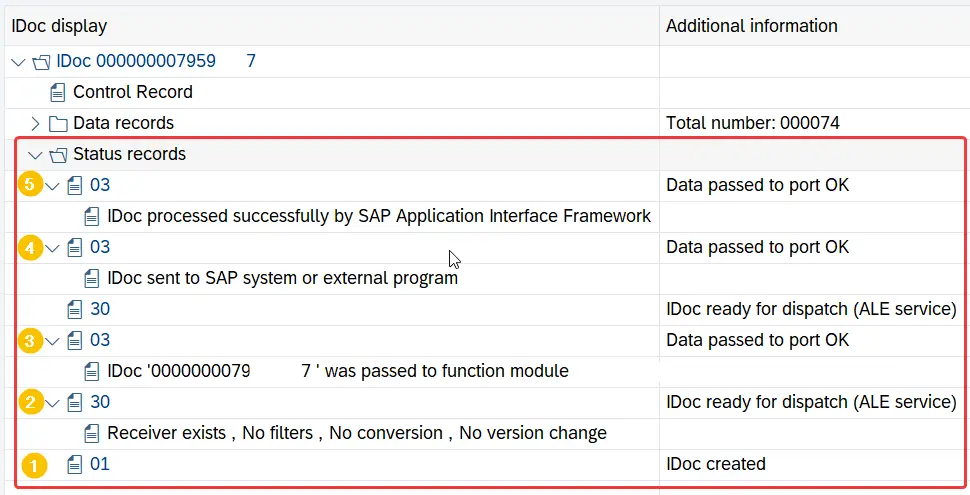
Notice the status of these iDocs. In this instance, Inbound iDoc has gone through 4 processing steps successfully. At the start, iDoc was created (status 50) and in the end iDoc successfully posted the application document (status 53).
The sample outbound iDoc has 5 statuses in its record: from iDoc creation (status 01) to iDoc being passed to the application Interface Framework (status 03).
iDoc Status Categories
Based on the iDoc status message type or severity, iDoc status codes can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Success
- Error
- Ready to process
- Warning
These categories tell you the overall status of the iDoc processing step: whether it was successful, ended up in an error, or was processed with warnings.
Additionally, there are certain status codes where iDoc is “ready to be processed” — these are intermediate steps before iDoc moves to the next processing step. For example, inbound iDocs in status 64 are ready to be processed by the application layer and post documents. Similarly, the iDoc status 03 of outbound iDocs is the status where iDoc is ready to be transferred to the external system.
Based on the message category of the last status code, the overall status of the iDoc is determined. If the final status of the iDoc is successful, the iDoc will be green; if the final status is an error, it will be red. Warning status or “ready to be processed” status will be marked in yellow.
Outbound iDoc Statuses
Outbound iDocs are iDocs going out of the system. The outbound iDoc statuses are between 01 and 49.
Here is a complete list of iDoc status codes with the description and their severity.
| Status Code | Status Description | Severity (Status Type) |
| 01 | IDoc created | Success |
| 02 | Error passing data to port | Error |
| 03 | Data passed to port OK | Success |
| 04 | Error within control information of EDI subsystem | Error |
| 05 | Translation error | Error |
| 06 | Translation OK | Success |
| 07 | Error during syntax check | Error |
| 08 | Syntax check OK | Success |
| 09 | Error during interchange handling | Error |
| 10 | Interchange handling OK | Success |
| 11 | Error during dispatch | Error |
| 12 | Dispatch OK | Success |
| 13 | Retransmission OK | Success |
| 14 | Interchange acknowledgment positive | Success |
| 15 | Interchange acknowledgment negative | Warning |
| 16 | Functional acknowledgment positive | Success |
| 17 | Functional acknowledgment negative | Warning |
| 18 | Triggering EDI subsystem OK | Success |
| 19 | Data passed to port for test | Success |
| 20 | Error triggering EDI subsystem | Error |
| 21 | Error passing data for test | Error |
| 22 | Dispatch OK, acknowledgment still due | Success |
| 23 | Error during retransmission | Error |
| 24 | Control information of EDI subsystem OK | Success |
| 25 | Processing despite syntax error (outbound) | Warning |
| 26 | Error during syntax check of IDoc (outbound) | Error |
| 27 | Error in dispatch level (ALE service) | Error |
| 28 | IDoc sent to ALE distribution unit retroactively | Success |
| 29 | Error in ALE service | Error |
| 30 | IDoc ready for dispatch (ALE service) | Success (Ready to be processed) |
| 31 | Error – no further processing | Error |
| 32 | IDoc was edited | Warning |
| 33 | Original of an IDoc which was edited | Warning |
| 34 | Error in control record of IDoc | Error |
| 35 | IDoc reloaded from archive | Success |
| 36 | Electronic signature not performed (timeout) | Error |
| 37 | Error when adding IDoc | Error |
| 38 | IDoc archived | Success |
| 39 | IDoc is in the target system (ALE service) | Success |
| 40 | Application document not created in target system | Error |
| 41 | Application document created in target system | Success |
| 42 | IDoc was created by test transaction | Warning/Information |
Inbound iDoc Statuses
Inbound iDocs are the iDocs that are coming into the system. The inbound iDoc statuses start from status 50.
| iDoc Status Code | Status Description | Severity (Status Type) |
| 50 | IDoc added | Success |
| 51 | Application document not posted | Error |
| 52 | Application document not fully posted | Warning |
| 53 | Application document posted | Success |
| 54 | Error during formal application check | Error |
| 55 | Formal application check OK | Success |
| 56 | IDoc with errors added | Error |
| 57 | Test IDoc: Error during application check | Error |
| 58 | IDoc copy from R/2 connection | Success |
| 59 | Not used | |
| 60 | Error during syntax check of IDoc (inbound) | Error |
| 61 | Processing despite syntax error (inbound) | Warning |
| 62 | IDoc passed to application | Success |
| 63 | Error passing IDoc to application | Error |
| 64 | IDoc ready to be passed to application | Success (Ready to be processed) |
| 65 | Error in ALE service | Error |
| 66 | IDoc is waiting for predecessor IDoc (serialization) | Warning |
| 67 | Not used | |
| 68 | Error – no further processing | Error |
| 69 | IDoc was edited | Warning |
| 70 | Original of an IDoc which was edited | Warning |
| 71 | IDoc reloaded from archive | Success |
| 72 | Not used, only R/2 | |
| 73 | IDoc archived | Success |
| 74 | IDoc was created by test transaction | Success |
| 75 | IDoc is in inbound queue | Success |
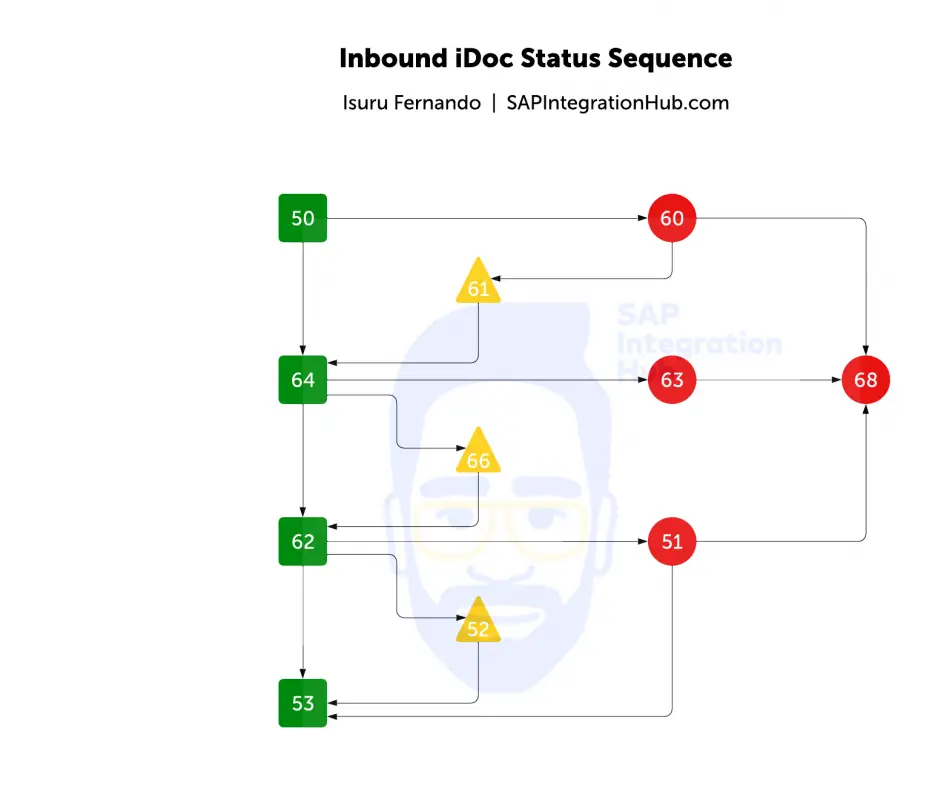
Sequence of Inbound iDoc Status
An inbound iDoc, when created in the system, has status 50. Then, depending on the partner profile setup, it gets processed immediately or collected. If the iDocs are collected, they will retain status 64 (“ready to be processed”) until they are processed.
Next, the iDoc passes to the application layer for processing. Application processing of an IDoc happens through a process code, a special functional module dedicated to iDoc processing depending on the iDoc type.
The final stage of an inbound iDoc processed without errors is status 53. However, if there are errors the iDoc goes into status 51.
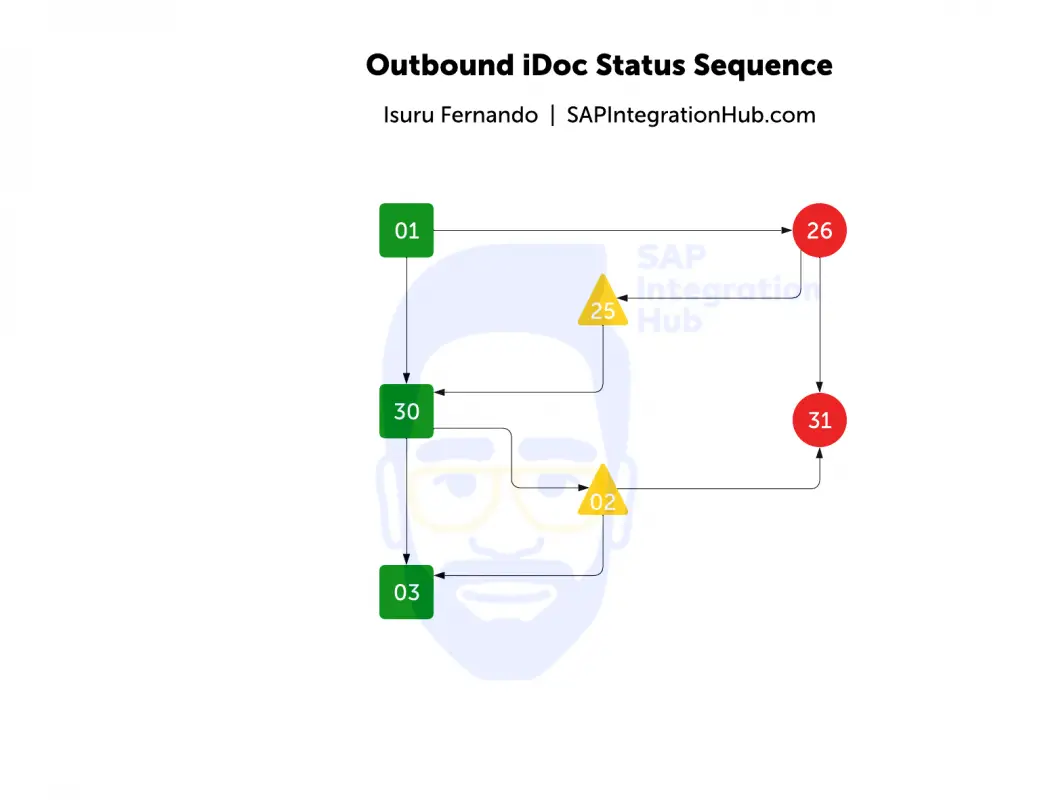
Sequence of Outbound iDoc Status
Outbound iDocs created in the system successfully, go into status 01. If there are no syntax errors the iDoc goes into status 30 (“iDoc ready to dispatch”). However, if there are syntax errors, iDoc will end up in status 26.
Outbound iDoc in status 30 can be processed using ABAP program or AIF to be transferred the next stage, status 03. Status 03 is usually the final state of the iDoc for the sender system — it denotes the iDoc has passed to the port successfully.
How to Monitor iDoc Statuses?
There are several ways to monitor the status of an iDoc in SAP S4 HANA. However, the monitoring method depends on the configuration of the SAP system and on the implemented iDoc monitoring capabilities.
For S4 HANA, it is recommended to use the SAP Application Integration Framework (AIF) for iDoc monitoring. But you can also use other standard tools, such as bd87, we02, etc. to view iDoc statuses.
Here are the transactions you can use to monitor iDocs in SAP S4 HANA:
- Standard iDoc monitoring tools: transactions bd87, we02, we05, etc.
- Application Integration Framework: transactions /n/aif/err, /n/aif/ifmon
Standard iDoc Monitoring
To view iDoc statuses, first go to transaction we02 or we05 and fill in the selection parameters to filter iDocs. Then, go to the status record section of the iDoc to view the history of iDoc statuses. The control record shows the final status of the iDoc.
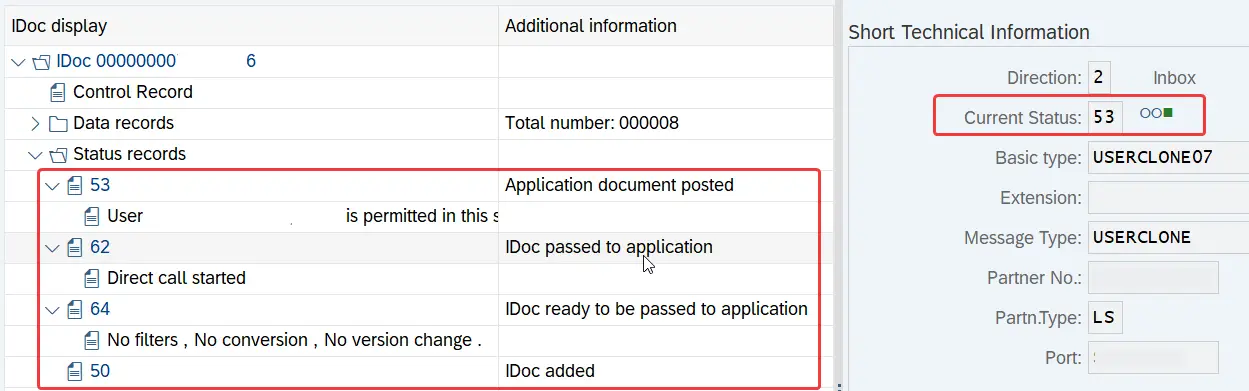
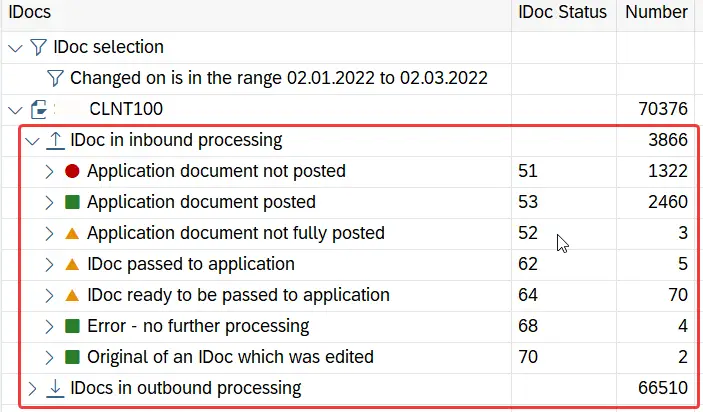
This method is not suitable if you have AIF functionalities, such as value mapping, fixed value mapping, and other transformations activated in AIF. In such a case, use aif/err or aif/ifmon transaction to monitor iDocs and check their statuses.
iDoc Monitoring using AIF
If you have implemented AIF for interface monitoring, you can use either SAP AIF Interface Monitor (transaction n/aif/ifmon) or SAP AIF Monitoring and Error Handling Tool (transaction /n/aif/err).
SAP AIF Interface Monitor – Transaction n/aif/ifmon
To get an overview of the iDoc processing status of all the interfaces in the SAP system, you can go to transaction /n/aif/ifmon. The /aif/ifmon displays the number of iDocs for each interface in one user-friendly dashboard. You can filter the display based on a date range and drill down to individual interfaces and iDocs directly from aif/ifmon.
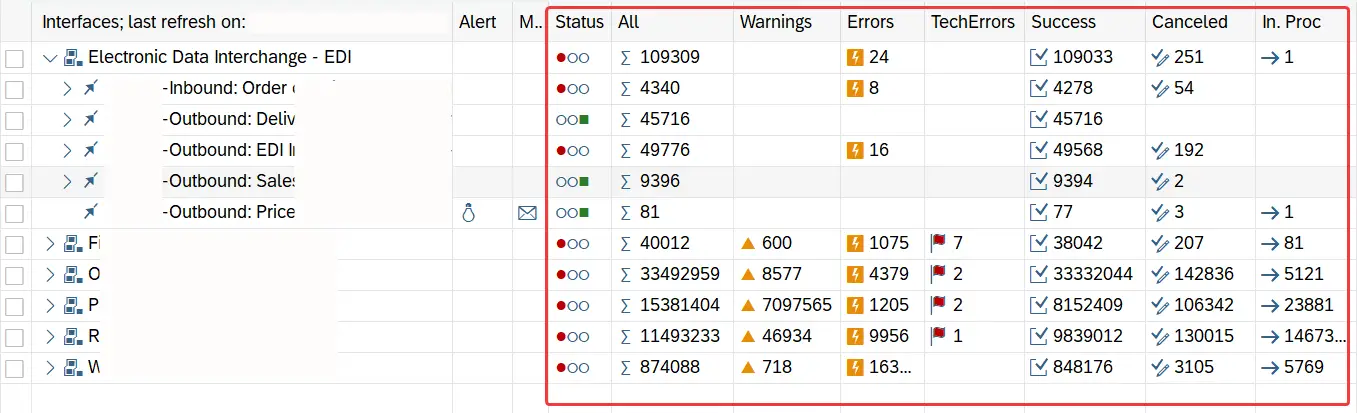
Additionally, AIF interface monitor has functionalities to mass-cancel messages, mass-reprocess messages and switch between different mail alert settings.
SAP AIF Monitoring and Error Handling Tool – Transaction /n/aif/err
/aif/err is a useful tool to check iDoc or any other interface messages statuses. Unlike ifmon, /aif/err has more options when it comes to filtering messages. For example, you can use message status, date range, interface-id, iDoc numbers, etc. for filtering.
You can also simulate iDoc processing functionality of AIF, such as value mapping, transformations, fixed value assignments, in /n/aif/err.
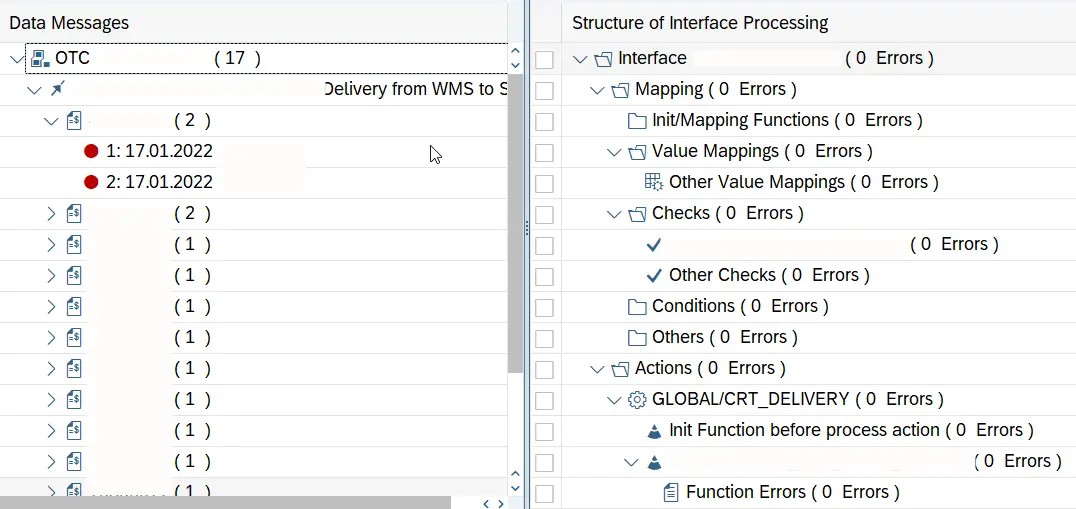
Moreover, you can add AIF custom functions to iDoc statuses.
How to Change the iDoc Status Manually?
Usually, when an iDoc is edited (content is modified), to correct erroneous data the iDoc goes into an edited status. When the content of an inbound iDoc is edited, it goes into status 69 (“iDoc was edited”). Similarly, when an outbound iDoc is edited, it goes into either status 32 or 33.
You cannot further process iDocs in the status “iDoc was edited”. Hence, you need to bring the iDoc to a “Ready to be processed” status. That is, status 64 for inbound iDocs and status 30 for outbound iDocs.
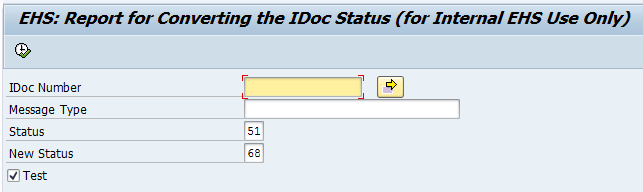
Use the standard program RC1_IDOC_SET_STATUS to change the statuses of edited iDocs.
To change the status of the iDoc, first, go to transaction se38; second, run the program RC1_IDOC_SET_STATUS. Then, enter the iDoc numbers, current status, and news status. Lastly, execute the program.
How to Reprocess iDocs in Error Statuses?
If an iDoc is in error status, you can use an appropriate method to reprocess the iDoc once the issues are sorted out.
In SAP S4 HANA you can reprocess iDocs in error statuses using the following methods:
- Status monitor for ALE messages – transaction BD87
- Application Integration Framework – transaction /AIF/ERR
- Standard iDoc processing programs
A Few Important iDoc Statuses
Here are some of the important iDoc statuses and the meaning behind them.
Status 53
When an inbound iDoc gets processed successfully in the application layer and posts the application document fully, the iDoc goes into status 53. This is usually the final status of the iDoc and no further processing is expected afterwards.
Status 51
When an inbound iDoc is not processed successfully in the application layer, the iDoc ends up in status 51. An iDoc can end up in status 51 due to multiple reasons: master data problems, wrong data values in the iDoc, or certain iDoc configuration issues.
iDocs in error status 51 and other error statuses can be reprocessed after the errors have been corrected using transactions bd87, /aif/err, or iDoc processing program RBDMANI2.
Status 64
When inbound iDocs come into the system they pass through status 64 and get transferred to application processing stage. If you have set the partner profile in transaction we20 as “collect iDoc”, the incoming iDocs will wait in yellow status 64 (“Ready to be processed”). You can use AIF, ABAP program, or bd87 to process iDocs in status 64.
Status 68
Status 68 stops the iDoc from being further processed by users or standard iDoc processing programs. However, you can use the program RC1_IDOC_SET_STATUS to change the iDoc status from 68 to 64, then run program RBDAPP01 to repost the iDoc.
If you have an iDoc that goes into an error status, such as 51, and the iDoc cannot be corrected to post the application document, set the iDoc to status 68. This allows you to post the application document manually and ignore the iDoc from being further processed by iDoc processing batch jobs.
Status 12
This is the consequence status of an outbound iDoc that goes through status 03. Status 03 tells us that iDoc has been passed to iDoc port successfully, that is, the iDoc was assigned to the tRFC queue. However, status 12 tells us that the iDoc has been transferred out of the tRFC queue and sent to the receiver system successfully.
Status 56
This status tells us that the incoming iDoc does not comply with the iDoc configuration. It could be an issue with partner profile settings or other iDoc configurations.
Check the iDoc configuration and rebuild the iDoc before processing.
SAP Tables iDoc Statuses are Stored
iDoc statuses records are saved mainly in two tables: EDIDC and EDIDS.
The current status of the iDoc can be found in the field “STATUS” of table EDIDC. The complete history of statuses of the iDoc is stored in EDIDS.
To summarize, we discussed the purpose of iDoc statuses and iDoc status record. Then, we listed down all the iDoc status codes of inbound and outbound iDocs. Next, we followed the sequence of iDoc statuses when iDoc is being processed. We also looked at how to monitor iDocs in SAP and how to change iDoc statuses. Finally, we went through several important iDoc statuses and their meaning.

Very informative article. Do you take any SAP Integration training?
Hello Mahesh,
I do have a course on “Cloud Integration with SAP Integration Suite”. This is a beginner-friendly course.
Check out the lesson plan here> https://sap-integration-hub.thinkific.com/courses/Cloud-Integration-with-SAP-Integration-Suite-for-beginners
Cheers!
Isuru
This blog was extremely helpful for someone new to SAP. It clarified my comprehension of the platform’s capabilities.
For the most part magnificent Article with heaps of accommodating information. I expect to peruse a lot more articles about Goodness, what an extraordinary blog entry! Your site has given the best information. This data is incredible. Your site is astounding and brilliant to visit.